Research Program
Introduction
Research program Sterile Science has been developed in an interdisciplinary collaboration across clinics and departments at Aalborg University Hospital, The National Center for Infection Control (CEI, SSI), and Danish Technological Institute, Aarhus.
The strategy is supported by an Advisory Board consisting of national and international experts in the field.
Research program Sterile Science contains a description of background, objectives, strategic research areas presented in two work packages, an action plan and an overview of the organization.
Background
The goal of reprocessing of sterilizable medical equipment is to avoid transmission of infection in connection with the use of reusable equipment and maximize the number of times these instruments can be used.
A prerequisite for securing that the reprocessing process leads to a sterile product depends on proper handling of the medical devices at all stages. The reprocessing process starts in the operating room, continues at the departments for Central Sterilization and in transit between them.
National and international recommendations in the field of reprocessing are built on professional recommendations, scientific literature, international guidelines and guidelines from relevant fields, and “best practice”. However, relevant evidence-based knowledge to support these recommendations is limited.
The program will provide evidence-based knowledge on reprocessing of sterilizable medical equipment. Based on this evidence the program management will be able to provide sound advice which can guide future recommendations in the area to improve quality, patient safety, sustainability, and cost-effectivity.
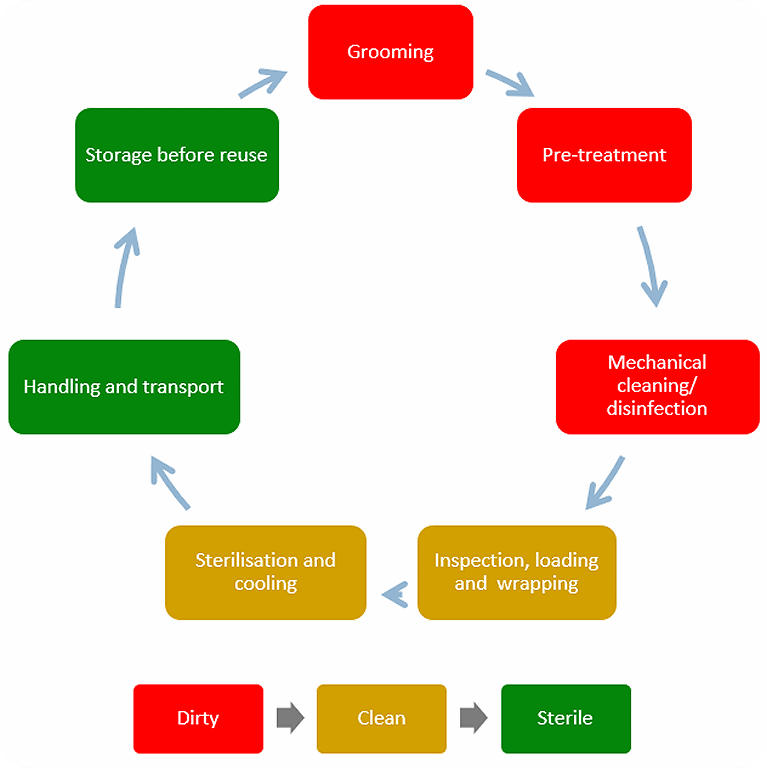
The reprocessing process
The reprocessing process includes grooming, pre-treatment, mechanical cleaning / disinfection, inspection, loading, wrapping, sterilization, handling and transport, as well as storage before reuse. A correct reprocessing also relies on trained and dedicated staff with clear responsibilities working in appropriate facilities.
Objective
The overall aim of the research program is to develop innovative strategies and new evidence on reprocessing of sterilizable medical equipment to improve quality, sustainability, and cost-effectivity in clinical practice. Based on this evidence the research program aims to document the effect and safety of the developed strategies and innovations and ensure their implementation in clinical practice.
Different approaches to develop new evidence, innovative strategies, and models on reprocessing of sterilizable medical equipment are investigated in two work packages.
Work Packages
Work package (WP) 1: Evidence-based clinical reprocessing practice
The aim of WP 1 is to produce clinical evidence-based knowledge on how the use of reusable surgical instruments can be optimized in relation to quality, sustainability, and cost-effectivity.
The clinical controlled research will focus on individual stages or across stages in the reprocessing process based on the processes related to grooming, pre-treatment, mechanical cleaning / disinfection, control, storage, packaging, sterilization, handling and transport, and / or storage before reprocessing.
Work package (WP) 2: Implementation – the effect on clinical practice
The aim of WP 2 is to produce follow up research on new opportunities arising from the clinical research performed in WP 1. Thus, research into implementation of evidence-based recommendations and the effects on availability and flexibility of instruments in surgical planning and reprocessing.
Opdateret